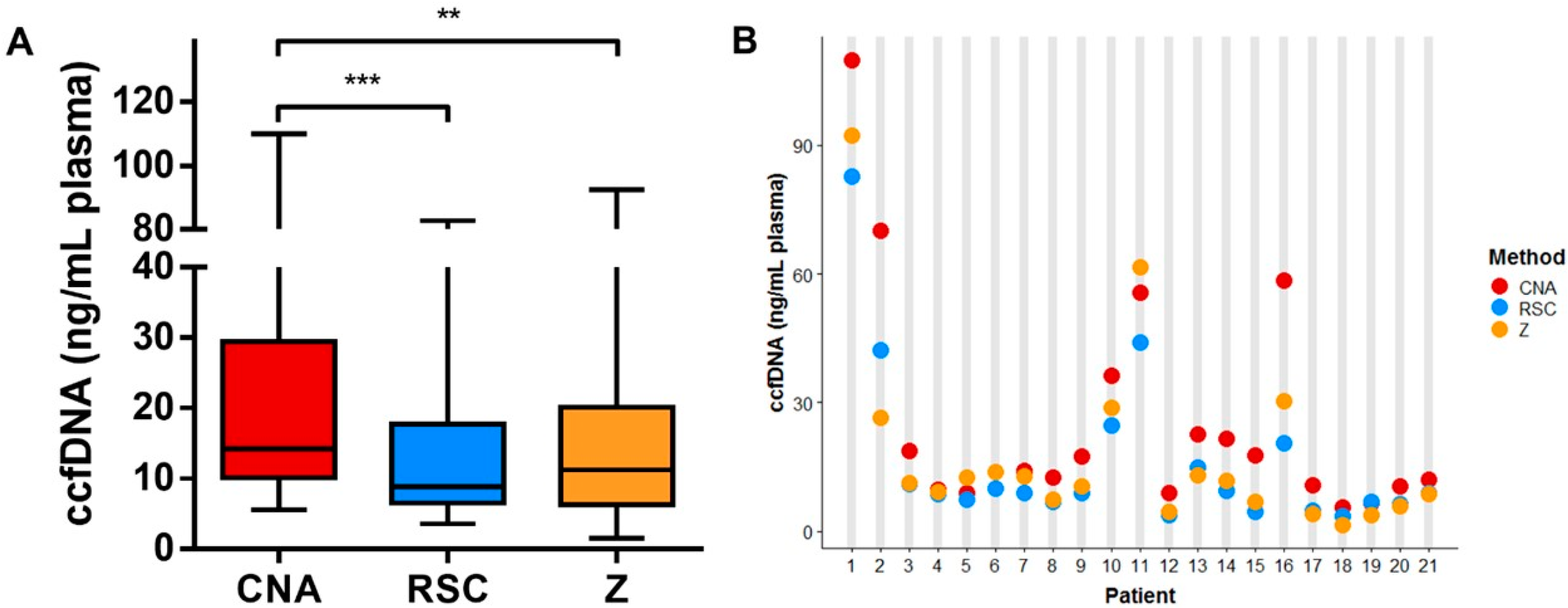
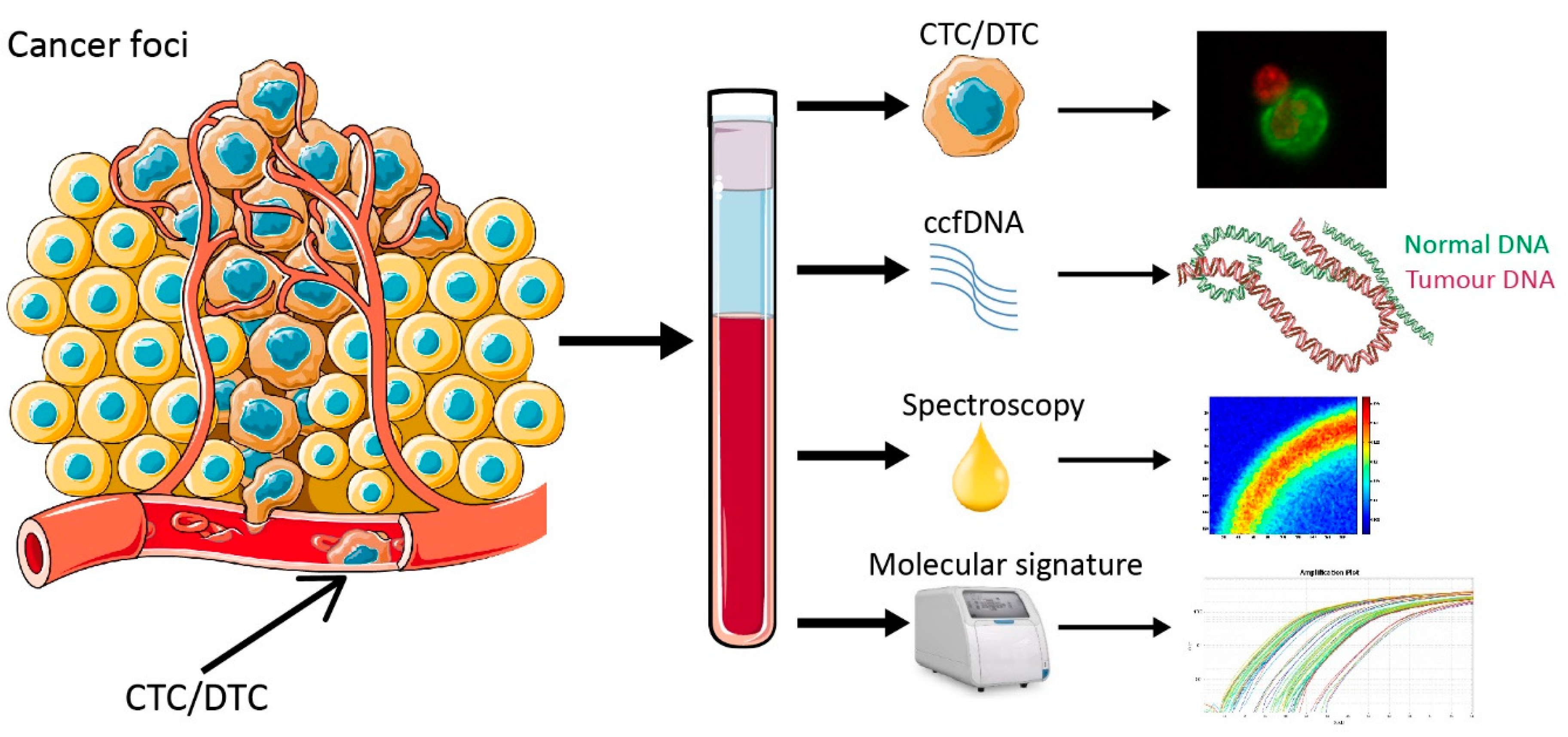
Sequencing Of Circulating Cell Free Dna During Pregnancy

Maternal blood is sampled by venipuncture.
Sequencing of circulating cell free dna during pregnancy. Cell free fetal dna cffdna is fetal dna that circulates freely in the maternal blood. Sequencing of cell free dna during pregnancy biology because they show that fetuses with rare autosomal trisomies can survive well into the third trimester. Two hours after delivery cffdna is no longer detectable in maternal blood. This review describes the basis.
Bianchi moderator sequencing of cell free dna cf dna circulating in the plasma of pregnant women to screen for the common fetal autosomal aneuploidies is the first widespread. Sequencing the fetal dna that circulates in a pregnant woman s blood holds promise for modern genomic medicine according to a review article by diana w. Fetal dna sequencing improves the accuracy of prenatal screening tests for genetic conditions and at times has led to the diagnosis of maternal conditions that may have otherwise gone undetected. Circulating cell free dna.
Bianchi m d a senior researcher and institute director at the national institutes of health and her colleague. Rare autosomal trisomies are also associated with poor obstetrical outcomes in cluding in utero growth restriction and stillbirth. Pertile md halks miller m flowers n barbacioru c kinnings sl vavrek d seltzer wk bianchi dw. Rare autosomal trisomies revealed by maternal plasma dna sequencing suggest increased risk of feto placental disease.
Bianchi m d a senior researcher and institute director at the national institutes of health and her colleague. Fetal chromosomal aneuploidy e g trisomy 21 monosomy x genomic sequence analysis panel circulating cell free fetal dna in maternal blood must include analysis of chromosomes 13 18 and 21. N engl j med. Analysis of cffdna is a method of non invasive prenatal diagnosis frequently ordered for pregnant women of advanced maternal age.
Alleles were present in the amplified cfdna and were consistent with the presence of ctdna originating from a molar pregnancy the percentage of dna attributable to the molar tissue was estimated by calculating the height of the peak s for the paternal allele s as a proportion of the sum of the allele heights for. Sequencing the fetal dna that circulates in a pregnant woman s blood holds promise for modern genomic medicine according to a review article by diana w. 2 issue 1 offers an international scope and provides an accurate presentation of data showing the value of cell free dna cfdna screenin.